Differences Between Rifles, Shotguns, and Handguns
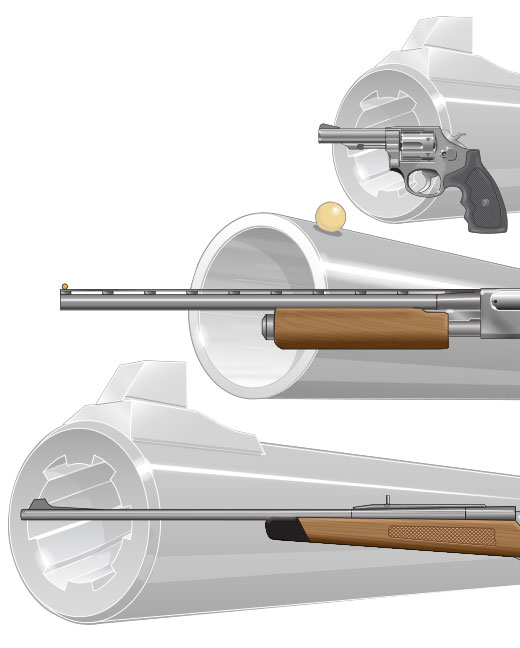
The main differences between rifles, shotguns, and handguns are their barrels, their intended targets, and the type of ammunition used.
- Rifle
- The rifle has a long barrel with rifling and thick walls to withstand high pressures. Rifling puts a spiral spin on a bullet fired from a rifle, increasing accuracy and distance.
- Rifles are typically used for firing at stationary targets.
- The bore of a rifle barrel is made for only one specific caliber of ammunition.
- Shotgun
- The shotgun has a long barrel and usually has a smooth bore to reduce friction. The barrel’s walls are thinner due to reduced pressures. If a shotgun is designed to fire slugs, it might have a rifled barrel.
- Shotguns are typically used for shooting at moving targets in the air.
- The bore of a shotgun barrel is made for only one specific gauge of ammunition.
- Handgun
- The handgun has a short barrel with rifling and thick walls to withstand high pressures. Because of the short barrel, extra care must be taken to control the muzzle of a handgun. Like the rifle, rifling in the handgun puts a spiral spin on a bullet when fired, increasing accuracy and distance.
- Handguns are typically used for firing at stationary targets.
- The bore of a handgun barrel is usually made for only one specific caliber of ammunition.